

The effectiveness of XA medium was compared to that of XLD using stock cultures and naturally contaminated food samples. This study yielded XA medium, which contains d-arabinose as a differential agent and neutral red as a pH indicator to differentiate Salmonella from Citrobacter freundii, Proteus mirabilis, and other enteric bacteria. Acid production by microorganisms in consequence of carbohydrate fermentation could inhibit hydrogen sulfide production ( 3). Hydrogen sulfide production depends on several factors, such as the sulfide production rate of the microorganisms, the oxygen concentration in the colony, pH, and the iron concentration in the medium ( 28). from Proteus spp., as well as from Citrobacter spp. Particularly, it is desirable to differentiate Salmonella spp. Recognizing the limits of currently used selective and differential media, it is desirable to improve the specificity and the sensitivity of the medium while maintaining cost-effectiveness. Also, chromogenic media are relatively expensive, making them less appropriate for routine laboratory use ( 24). Although chromogenic media have higher specificities than conventional media, some of them have a low sensitivity ( 10, 13, 30), which results in more false negatives observed on these media. These media incorporate chromogenic substrates which are metabolized by Salmonella spp. Several chromogenic media have been developed to increase the specificity of conventional selective and differential media for the detection of Salmonella spp. However, BS agar has several disadvantages, such as low sensitivity and long incubation time for development of the characteristic colony morphology ( 18).
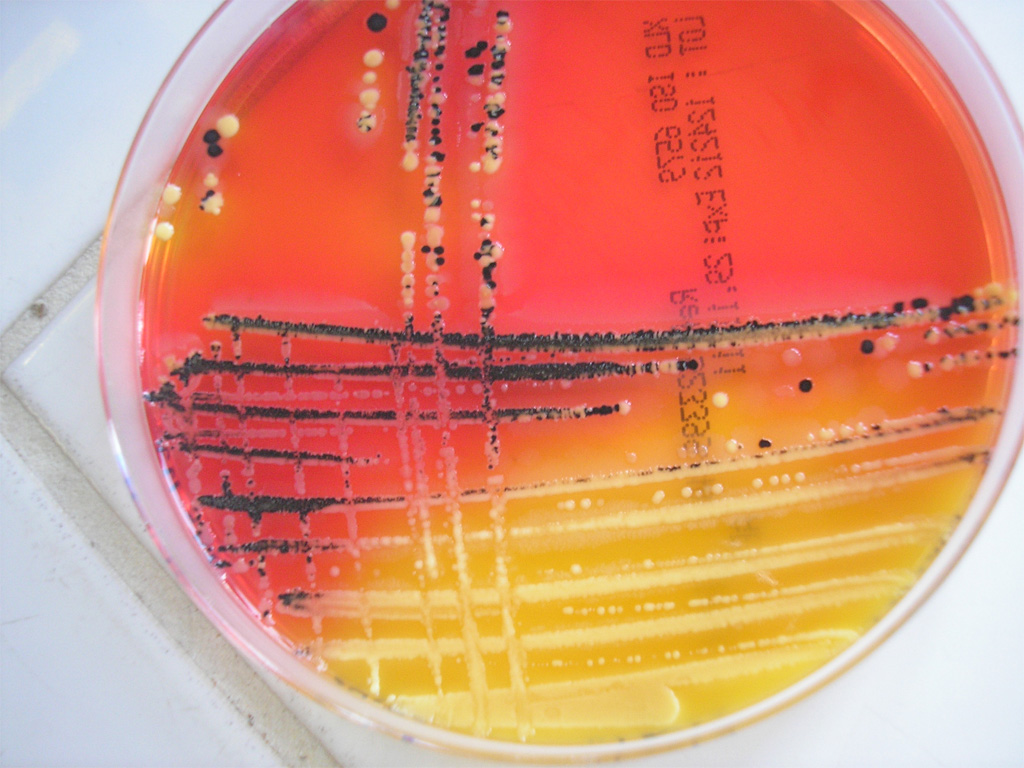

BS agar is the medium of choice for the isolation of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi, and it is used for the isolation of atypical salmonellae, such as those which ferment lactose ( 7). Thus, numerous false-positive results are observed on these media which require further confirmation testing, a time-consuming and labor-intensive activity ( 13). However, these characteristics are shared with other microorganisms, such as Proteus and Citrobacter ( 11, 32). XLD and HE agar are the most popular media for isolating Salmonella spp., and their differentiation abilities rely on characteristics of Salmonella, such as hydrogen sulfide production and the nonfermentation of lactose ( 28). A wide variety of selective and differential media has been developed for this purpose, including xylose lysine desoxycholate agar (XLD), Hektoen enteric (HE) agar, and bismuth sulfite (BS) agar ( 6). The use of selective and differential plating media is a simple method for the isolation of Salmonella spp. The choice of a suitable sampling procedure combined with a sensitive culture method is important for the successful detection of Salmonella ( 4). from various foods are important to ensure food quality and safety. Thus, effective methods for the isolation of Salmonella spp. Various foods, such as chicken, beef, and pork, have been implicated in outbreaks caused by Salmonella spp. It is the cause of an estimated 1.4 million illnesses annually in the United States ( 25). Salmonella has been associated with many food-borne diseases across the world ( 19). On the basis of its good specificity, XA medium is useful for the isolation of Salmonella spp. The specificity of XA medium (92.0%) was superior to that of XLD (73.0%), with a total of 14 and 47 false-positive results found on XA medium and XLD, respectively. The sensitivities of XA medium and XLD were equal (100%), and a total of 6 Salmonella strains were isolated from the 180 food samples. In the second phase of the study, a total of 180 food samples were cultured onto XA medium and XLD after selective enrichment. mirabilis appeared as black colonies on XA medium. Citrobacter freundii ( n = 21) and Proteus mirabilis ( n = 21) stock cultures produced black colonies on XLD, whereas only 4 strains of P. The sensitivities of XA medium and XLD were identical (92.7%). The remaining 6 strains belonged to Salmonella enterica serovars Berta ( n = 1), Paratyphi A ( n = 1), Gallinarum ( n = 2), and Pullorum ( n = 2). tested, 76 produced a characteristic black colony on XA medium and XLD. XA medium and XLD were evaluated with a total of 82 Salmonella and 69 non- Salmonella stock cultures. The sensitivity and the specificity of XA medium were compared to those of xylose lysine desoxycholate agar (XLD) using stock cultures and naturally contaminated food samples. We describe an improved selective, differential, and cost-effective medium, XA medium, which contains d-arabinose, to facilitate the selective isolation of Salmonella spp.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
